Definition Of Tsunami:
A tsunami is a series of waves that commence due to an earthquake, underwater volcanic eruption, landslide, or other abrupt disturbance.
Meaning Of the Word Tsunami:
The term tsunami comes from a Japanese word, Tsu: port, Nami: wave. Tsunami means harbor wave.
Causes Of Tsunami:
- Submarine Tectonic Earthquakes:
It is the earthquake on the ocean floor and is the main cause of Tsunamis. It is the displacement of the tectonic plates on the ocean floor that moves a larger volume of water, resulting in high-energy waves. A tsunami is produced by an earthquake of ~7.0 magnitude or greater by the vertical displacement of seawater.
- Volcanic Activity:
A tsunami is produced by a volcanic eruption underwater or near the sea. The explosion causes a greater volume displacement.
- Submarine Landslides:
The movement of rock or soil on the ocean floor displaces seawater, triggering a tsunami. These landslides can be caused by an earthquake, volcanic activity, or many other reasons.
Mechanism of Tsunami:
The tectonic plates of the Earth’s surface slip, releasing a massive amount of energy underwater.
This energy travels vertically up to the surface, displacing water and raising it above the normal sea level.
The gravity pulls that energy back; the energy ripples outward horizontally, generating a tsunami.
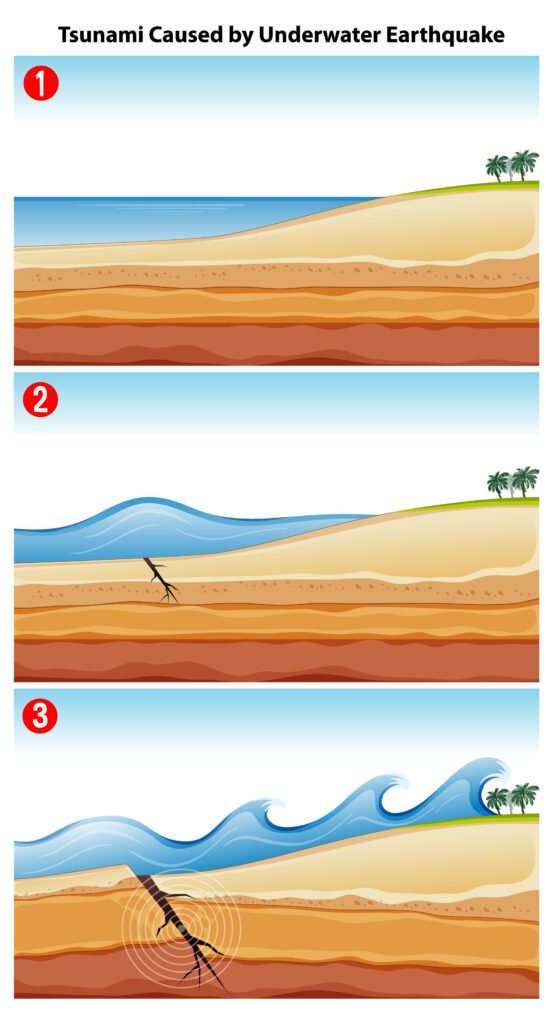
Physical Characteristics of Tsunami:
Tsunami waves are low in height and are at high speed at the point of their generation, with energy distributed widely. But at the coast, the waves are up to 30 km high and are at low speed,d that causes destruction. The waves occur in a series, and the serial wave generation is a repeated and prolonged process.
Classification of Tsunami:
Tsunamis are of three types based on location:
- Local Tsunami:
A tsunami generated near the coast. It takes a few minutes to reach the shore. It affects a localized area. The causes of generation may be a submarine landslide or an earthquake.
- Regional Tsunami:
A tsunami affecting a greater region, such as a country. It takes a few hours to reach the nearby countries.
- Distant Tsunami:
A tsunami that travels thousands of kilometers. This type of tsunami has global impacts.
Consequences of Tsunami:
- Death:
The approach of a tsunami with no or few early warning signs causes one hundred casualties. These casualties might occur due to drowning, infrastructure collapse, explosions, and floating debris.
- Destruction:
Large objects, such as buildings and objects, are destroyed because of heavy waves and are transformed into skeletal structures. The harbor materials are forced inland, causing massive destruction.
- Diseases:
The contamination of water due to the waste management sites’ collapses, and floating debris, along with the mixed sewage water with ocean water, leads to the outbreak of diseases such as Cholera.
Environmental Impacts of Tsunami:
- Tsunamis not only impact humans but also the animals and plants.
- The trees and plants are uprooted due to heavy winds and waves.
- Animals are killed due to drowning in water.
- The solid waste handling, recycling, disposal, and storage are the most critical problems to be solved by the tsunami-hit nations.
Examples:
- The most powerful Tsunami in the USA was caused by a magnitude of 9.2 in Alaska in 1964. 139 people were killed by the infrastructure collapse and the burning of oil storage tanks.
- The Japan tsunami in 2011 was one of the most destructive! It was caused because of an earthquake underwater, resulting in huge waves of around 133 feet. 15,000 people lost their lives, and the Fukushima nuclear plant was also destroyed.
- The Indian Ocean tsunami of 2004 killed 225,000 people in 14 countries, including Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and Thailand. It also commenced due to an earthquake and resulted in waves up to 100 feet tall.
Some Other Blogs:
Check out this blog on Criteria Air Pollutants












