What is Carbon Sequestration?
Carbon sequestration refers to a procedure of absorbing more carbon dioxide gas from the atmosphere than it liberates. It stores carbon dioxide gas and reduces greenhouse gases.
Types Of Carbon Sequestration:
Carbon sequestration is of two types:
- Natural carbon sequestrators
- Artificial carbon sequestrators
Natural carbon sequestrators include the forests, oceans, and soils.
- Oceans: The largest carbon sequestrator that absorbs carbon dioxide via physical and biological processes.
- Forests: Absorb the CO2 from the atmosphere via Photosynthesis.
- Soil: It absorbs the CO2 in the deep-rooted system of plants.
An artificial carbon sequestrator includes the technological system of CCS (which captures the CO2 gas from the atmosphere and stores it underground).
In this blog, we’ll be discussing forests as the second major carbon sequestrator in terms of capacity which plays a crucial role in climate change mitigation.
Mechanism Of Carbon Sequestration By Forests:
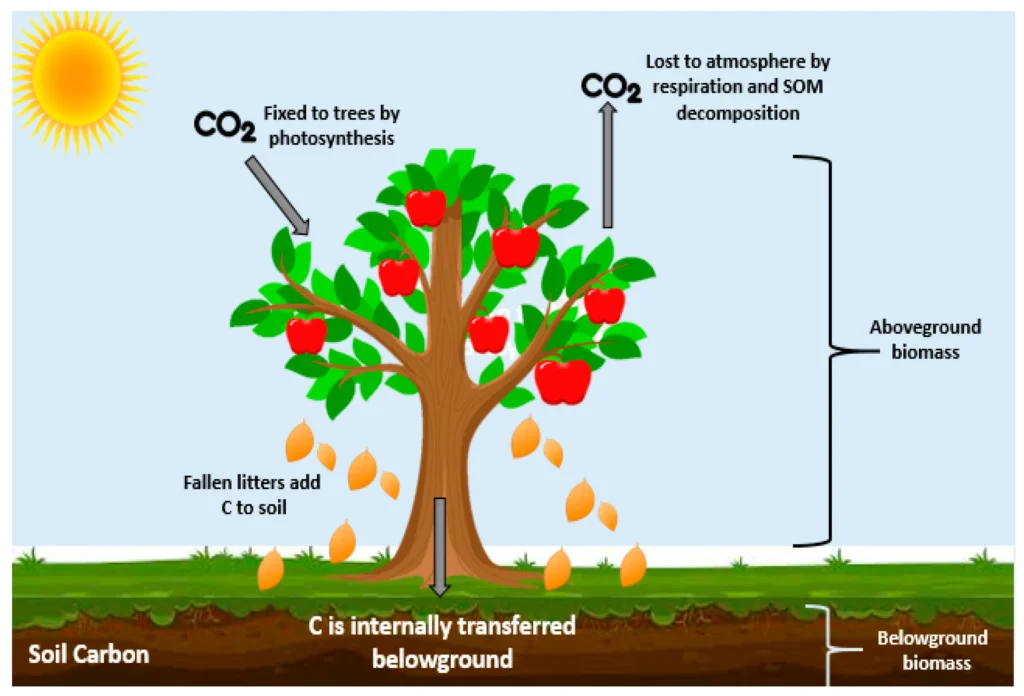
Forests exist everywhere globally. They play a vital role as a carbon sequestrator through a process known as PHOTOSYNTHESIS.
Photosynthesis involves the exchange of gases between the atmosphere and the trees. Plants absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and convert it into energy material (glucose), storing it in the trunks, leaves, branches, and soil in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll. Trees release oxygen as a byproduct, which humans inhale.
6CO2 + 6H2O …sunlight and chlorophyll…> C6H12O6 + 6O2 + energy
The carbon is long-term stored within plants and trees and in the soil, making forests a dominant source of carbon sequestration.
How do forests act as a Climate Change Mitigator?
- Forests can absorb Carbon dioxide gas from the atmosphere, which serves as a major greenhouse gas, and store it as biomass in the tree trunks, branches, leaves, and dead organic matter.
- This carbon storage capacity reduces the load of greenhouse gases whilst mitigating the climate change issue and Global warming.
- They keep the air quality excellent and maintain the cooling effect.
- Forests also regulate the water cycle, balancing condensation and weather patterns.
- They protect the soil and conserve biodiversity.
The major drawback is; if the tree dies or burns, the stored carbon is released into the atmosphere.
Human activities that affect the forests.
Anthropogenic activities such as Deforestation, Urbanization, Agricultural activities, and logging can lead to the demolition and destruction of forests. Fewer forests mean less carbon sequestration and Increased Global Warming.
Solution Measures need to be taken:
It’s crucial to increase activities like afforestation, reforestation, and protection of old forests so that the forests are kept conserved and a slight hope for a better environment remains alive.
A Wise Quote:
The best time to plant trees was 20 years ago. The second-best time is now.
A Related Blog Post:
Check out our blog on CloudBursts, which is also a cause of Global Warming…












