What Is An Ecosystem?
Ecosystem Definition:
Earth is our belonging that sustains the life of all forms by providing favorable circumstances. The Earth is, on the whole, composed of an Ecosystem (the interconnection of biotic components with each other and with the abiotic components).
Spheres Of The Ecosystem:
The ecosystem encompasses 4 spheres, namely;
- Atmosphere
- Lithosphere
- Hydrosphere
- Biosphere
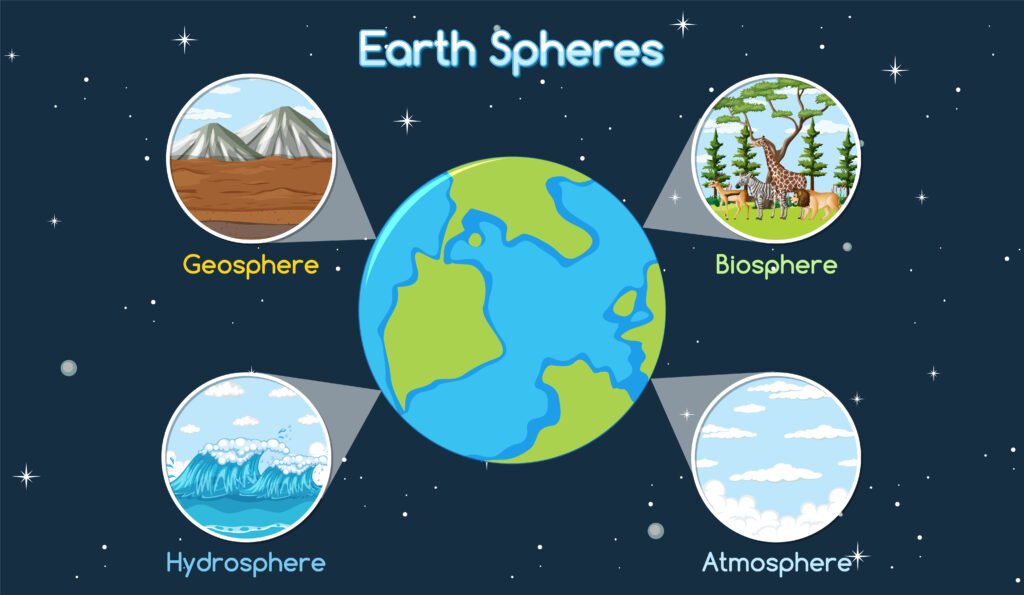
Earth is what sustains the life of all by providing favorable conditions. The Earth is composed of an ecosystem of interconnected biotic and abiotic components.
There exists a distinct sphere named Anthro-sphere (the part of the environment influenced by human activities.)
All living organisms in the ecosystem are afflicted by the act of each sphere; this effectiveness can either be constructive or destructive. These spheres in the ecosystem are interconnected or interrelated to one another, i.e., the activities befalling in one sphere possess express or implied impact on another.
But how?
For Instance:
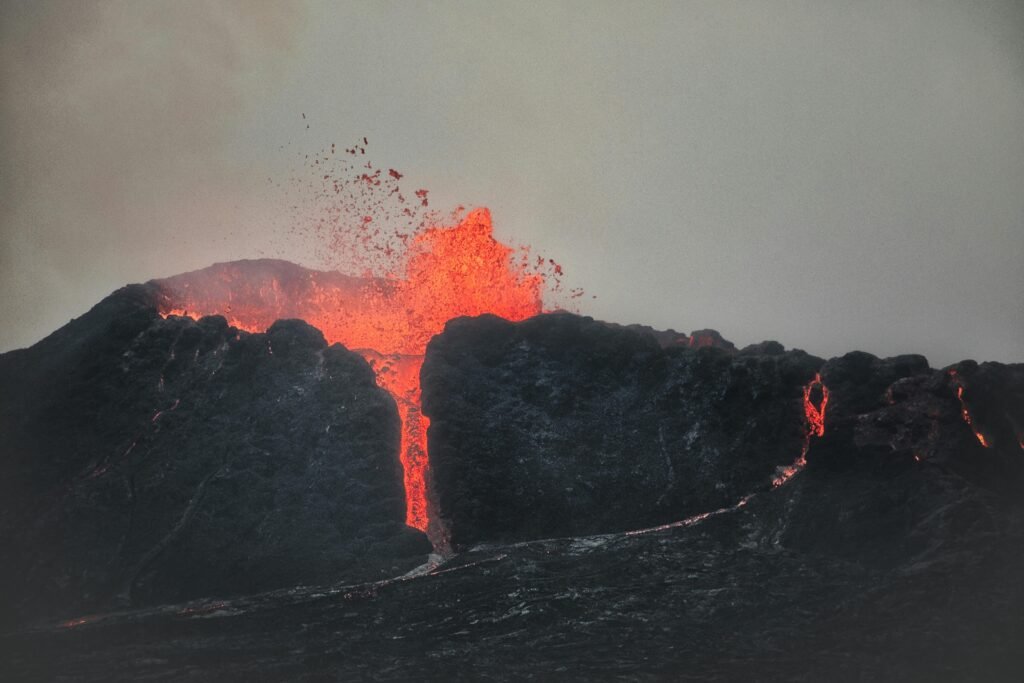
- Lithosphere and Atmosphere: Volcanic eruptions deteriorate the air quality and release harmful gases and ashes.

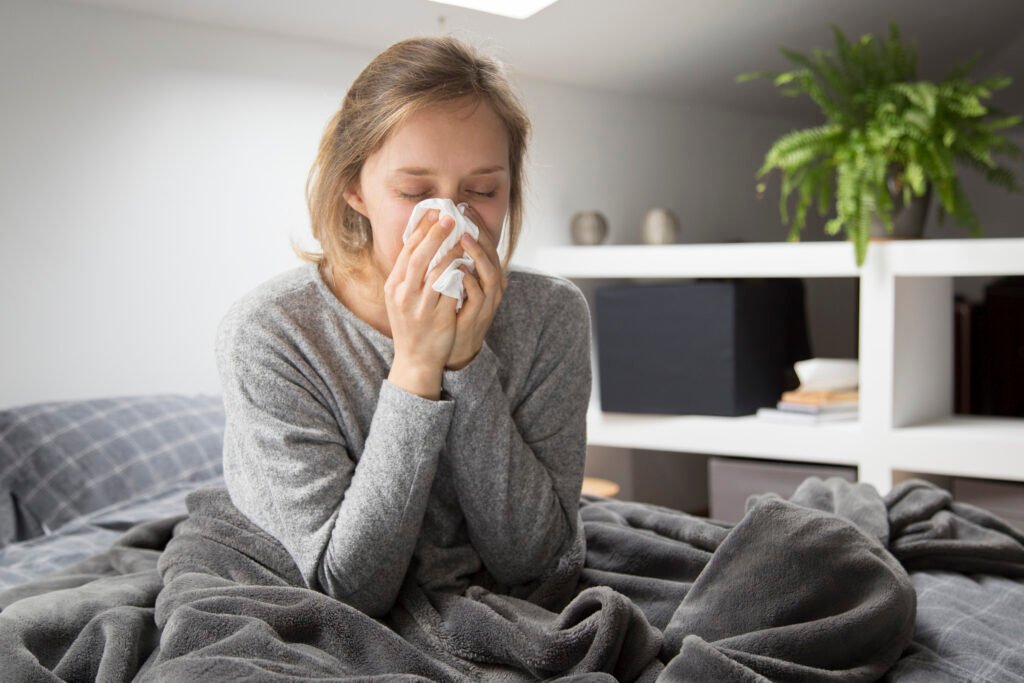
- Biosphere and Atmosphere: Living beings release droplets by coughing or sneezing that get dispersed in the air and travel long distances, indirectly affecting other living beings.

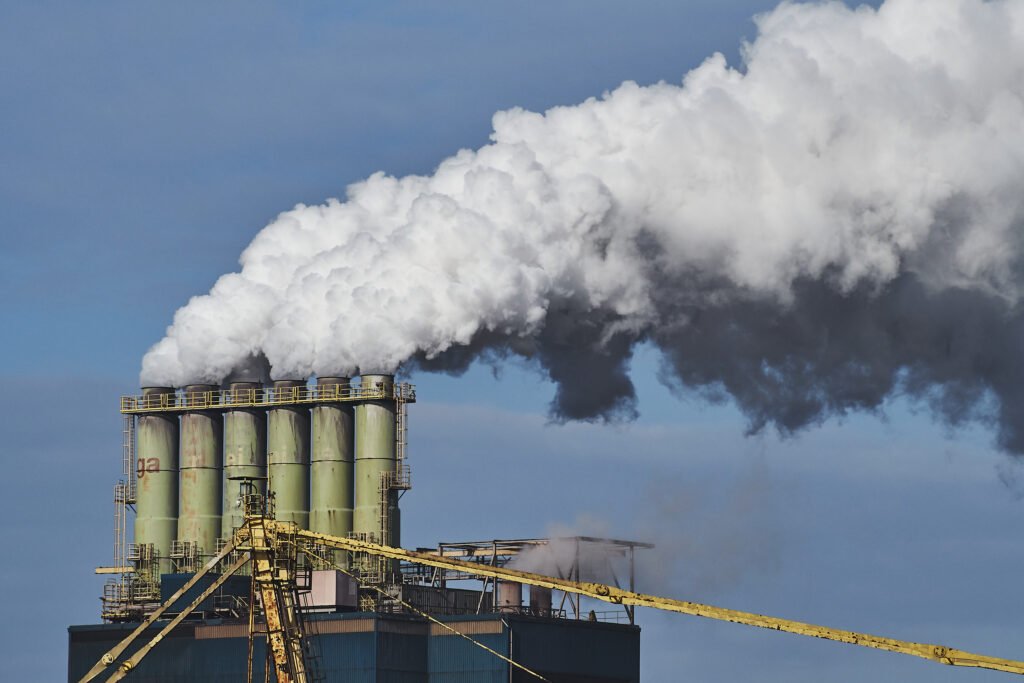
- Atmosphere and Hydrosphere: Harmful gases like NOx and SOx are released by fossil fuel burning via automobiles and power plants into the air. The Sox and Nox, when precipitated from the sky, get into the hydrosphere, leading to the acidification of oceans and disruption of food chains.

- Biosphere and Hydrosphere: The agricultural runoff of fertilizers and pesticides causes eutrophication and oxygen depletion in the water bodies.

- Biosphere and Atmosphere: Deforestation by human beings causes increased levels of CO2 and climate imbalances.

- Lithosphere and Biosphere: Mining by human beings to extract resources from underground leads to soil infertility and degradation, and habitat destruction.

There are one hundred examples; some are discussed above. The considerable negative impacts are owing to the Anthro sphere, headed by human beings themselves. This displays the clarity of how everything is continual and persists on Earth. Earth itself is a closed ecosystem from which the transference of energy may take place, but not the mass.
So, whatever you generate today will return to you tomorrow in a distinguished form, appearance, and way.
Conclusion:
“Every sphere is either directly or indirectly connected and interrelated to one another.”
Related Blog:
What is Global Warming?












